Advanced AI and Data Science Roadmap for Job-Ready Professionals (2026 Guide)
Breaking into AI and Data Science sounds exciting. But for most learners, it becomes confusing, frustrating, and overwhelming.
You start with Python.
Then someone says, “Learn SQL first.”
Another says, “No, jump into Machine Learning.”
Soon, you are stuck in tutorial hell with certificates but no one is offering you job.
This guide solves that problem.
This is a clear, advanced AI and Data Science roadmap designed to make you job-ready, not just course-ready. It is based on industry requirements, real hiring trends and skills companies actually test.
What Does “Job-Ready” Mean in AI and Data Science?
Being job-ready does not mean:
- Completing 20 online courses
- Knowing every algorithm by name
- Memorizing theory without practice
Being job-ready means:
- You can solve real problems with data
- You can explain your thinking clearly
- You can build, evaluate, and deploy models
- You understand business impact, not just code
Recruiters look for proof of skills, not just learning effort.
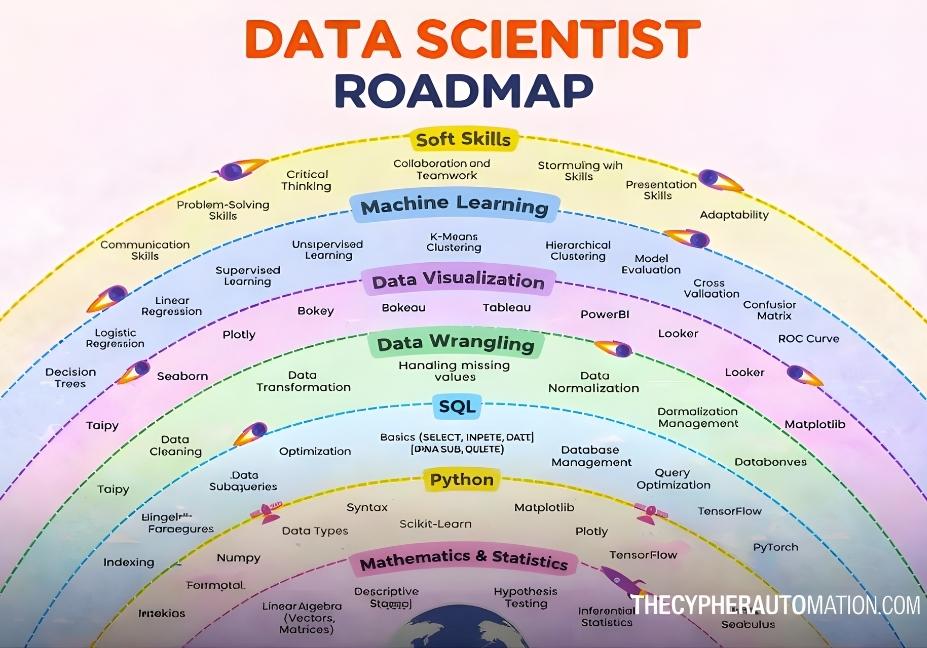
Foundation Layer: Mathematics and Statistics (The Backbone)
Many beginners skip math. That is a big mistake.
You don’t need PhD-level math—but you must understand how models work.
Core Topics You Must Know
- Linear algebra (vectors, matrices)
- Probability and distributions
- Mean, median, variance, standard deviation
- Hypothesis testing
- Basic calculus for optimization
Why This Matters in Real Jobs
Math helps you:
- Choose the right model
- Understand model performance
- Reduce bias and overfitting
- Explain results confidently in interviews
A data scientist who understands math is trusted more.
Complete AI & Data Science Roadmap Table
| Layer / Skill Area | Key Topics & Tools | Purpose / Outcome | Recommended Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics & Statistics | Linear Algebra (vectors, matrices), Probability & Distributions, Descriptive & Inferential Statistics, Hypothesis Testing, Calculus | Understand model behavior, feature importance, and evaluation metrics | Beginner → Intermediate |
| Python Programming | Syntax, Control Structures, Data Types, Functions, OOP, Libraries: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch | Write clean code, manipulate data, and build machine learning models | Beginner → Intermediate |
| SQL & Databases | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, Joins, Subqueries, Window Functions, Indexing, Query Optimization, Stored Procedures | Extract, clean, and prepare datasets from real-world databases | Beginner → Intermediate |
| Data Wrangling & Feature Engineering | Data Cleaning, Missing Values Handling, Outlier Detection, Data Transformation, Normalization, Feature Selection, Feature Creation | Prepare high-quality datasets and improve model accuracy | Intermediate |
| Data Visualization & Storytelling | Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly, Tableau, Power BI, Looker, Dashboard Design, Executive Presentations | Communicate insights effectively and support business decisions | Beginner → Advanced |
| Machine Learning | Supervised Learning: Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest | Unsupervised Learning: K-Means, Hierarchical Clustering | Model Evaluation: Cross-Validation, Confusion Matrix, ROC Curve |
| Advanced AI & Deep Learning | Neural Networks, CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, Transformers, NLP, Computer Vision, Recommendation Systems | Build AI solutions and specialize in high-demand AI roles | Advanced |
| MLOps & Deployment | Model Versioning, APIs (Flask/FastAPI), Cloud Basics (AWS/GCP/Azure), Monitoring, CI/CD | Deploy models in production and scale AI solutions | Advanced |
| Soft Skills | Communication, Collaboration, Problem-Solving, Critical Thinking, Adaptability | Explain insights, work in teams, and improve hiring potential | All Levels |
| Projects | End-to-End ML Project, SQL Analytics Project, Interactive Dashboards, Deployed AI Model | Build a portfolio to demonstrate real-world skills | All Levels |
Programming Core: Python for Data Science and AI
Python is the main language for AI and Data Science.
You don’t need to know everything—but you must be comfortable and clean.
Python Skills Recruiters Expect
- Variables, loops, functions
- Lists, dictionaries, sets
- Object-oriented programming (OOP)
- Writing readable, reusable code
Essential Libraries in AI and Data Science Roadmap
- NumPy – numerical computing
- Pandas – data manipulation
- Matplotlib & Seaborn – data visualization
- Scikit-learn – machine learning
- TensorFlow / PyTorch – deep learning
Python is not just a tool. It is your thinking language.
SQL Mastery: Data Extraction Like a Professional
Most real data lives in databases, not CSV files.
If you ignore SQL, you limit your career.
Must-Know SQL Concepts
- SELECT, WHERE, ORDER BY
- GROUP BY, HAVING
- INNER, LEFT, RIGHT joins
- Subqueries
- Window functions
- Basic query optimization
SQL is heavily tested in data science interviews, especially for analytics roles.
Data Wrangling and Feature Engineering (Where Real Work Happens)
This is where 80% of a data scientist’s time goes.
Key Data Wrangling Skills
- Handling missing values
- Removing duplicates
- Detecting outliers
- Scaling and normalizing data
Feature Engineering Skills
- Encoding categorical variables
- Feature selection
- Feature creation from raw data
Good features often matter more than complex models.
Data Visualization and Business Storytelling AI and Data Science Roadmap
A great model is useless if people don’t understand it.
Tools Used in Industry
- Matplotlib & Seaborn
- Plotly
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Looker
Why Storytelling Matters
Companies don’t hire data scientists for charts.
They hire them for decisions.
You must explain:
- What happened
- Why it happened
- What should be done next
This skill separates junior from senior roles.
Machine Learning: From Theory to Real Impact
Machine learning turns data into predictions.
Supervised Learning
- Linear regression
- Logistic regression
- Decision trees
- Random forest
- Gradient boosting
Unsupervised Learning
- K-means clustering
- Hierarchical clustering
- PCA (dimensionality reduction)
Model Evaluation
- Accuracy, precision, recall
- F1-score
- ROC-AUC
- Cross-validation
Knowing when to use a model matters more than knowing many models.
Advanced AI and Deep Learning Skills
Once ML fundamentals are strong, move to advanced AI.
Core Deep Learning Concepts
- Neural networks
- Backpropagation
- CNNs (computer vision)
- RNNs and LSTMs
- Transformers (basic understanding)
AI Specialization Areas
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Recommendation systems
- Generative AI basics
Specialization increases salary and demand.
MLOps and Deployment (The Job-Ready Difference)
Most learners stop at training models. Companies don’t.
Deployment Skills
- Saving and loading models
- Building APIs (Flask or FastAPI)
- Basic Docker knowledge
- Cloud basics (AWS, GCP, Azure)
Monitoring and Scaling
- Model drift detection
- Performance monitoring
- Version control for ML models
This is what makes you industry-ready, not just skilled.
Soft Skills That Get You Hired Faster
Soft skills are not optional.
You must have:
- Clear communication
- Problem-solving mindset
- Business understanding
- Team collaboration
- Adaptability
Many technically strong candidates fail interviews due to poor explanation.
Projects You Must Build to Be Job-Ready
Projects prove your skills.
You should have:
- End-to-end machine learning project
- SQL + analytics project
- Data visualization dashboard
- One deployed AI model
- Clean GitHub portfolio
Example Project Roadmap Table
| Skill Area | Project Example | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Python & Pandas | Data cleaning pipeline | Structured dataset |
| SQL | Business query analysis | Actionable insights |
| Visualization | Interactive dashboard | Decision support |
| Machine Learning | Prediction model | Measured performance |
| Deployment | Model API | Real-world usage |
Projects build trust with recruiters.
Data Science Interview Preparation Roadmap
Interviews usually include:
- Python coding questions
- SQL queries
- Statistics and ML theory
- Case studies
- Project discussions
Prepare by:
- Practicing real problems
- Explaining your thinking
- Improving your portfolio story
Confidence comes from practice, not memorization.
AI Engineer vs Data Scientist: Which Path Should You Choose?
Data Scientist
- Focus: insights, models, analysis
- Skills: stats, ML, SQL, storytelling
AI / ML Engineer
- Focus: systems, deployment, scale
- Skills: deep learning, MLOps, cloud
Choose based on your interest, not hype.
Common Mistakes That Stop People from Getting Hired
Avoid these:
- Learning tools without basics
- Skipping projects
- Ignoring math and SQL
- Not building a portfolio
- Waiting for “perfect time”
Progress beats perfection.
Final Action Plan: 6 to 12 Month Job-Ready Strategy
- Months 1–3: Foundations + Python + SQL
- Months 4–6: Data wrangling, visualization, ML
- Months 7–9: Advanced AI + projects
- Months 10–12: Deployment + interview prep
Even 1–2 hours daily is enough with the right structure.
Conclusion: From Learning AI to Working in AI
AI and Data Science are not hard.
They are poorly structured for beginners.
With the right roadmap:
- You learn faster
- You build confidence
- You become job-ready
Focus on skills, projects, and clarity—and the results will follow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to become job-ready in AI and Data Science?
Most learners become job-ready in 6 to 12 months with consistent practice. The exact time depends on your background, learning speed, and how many real-world projects you build.
2. Do I need a degree to get a job in Data Science or AI?
No, a degree is not mandatory. Many companies focus on skills, projects, and problem-solving ability. A strong portfolio and practical experience often matter more than formal education.
3. Is Data Science still a good career in 2026?
Yes. Data Science and AI continue to grow due to automation, AI adoption, and data-driven decision-making. Professionals with advanced skills and deployment knowledge remain in high demand.
4. What skills are most important to become job-ready in Data Science?
The most important skills include:
- Python and SQL
- Statistics and mathematics
- Data cleaning and feature engineering
- Machine learning models
- Data visualization and storytelling
- Real-world project experience
5. Should I learn AI or Data Science first?
Start with Data Science fundamentals like Python, statistics, and SQL. These skills create a strong base. Once comfortable, move into advanced AI and machine learning topics.
6. Is machine learning required for all Data Science jobs?
Not always. Entry-level data analyst roles may focus more on SQL, Python, and visualization. However, machine learning is essential for advanced and high-paying roles.
7. What projects should I build to get hired as a Data Scientist?
You should build:
- End-to-end data analysis projects
- Machine learning prediction models
- Business dashboards
- One deployed model using an API
Projects should solve real problems, not just tutorial datasets.
8. Is SQL more important than Python for Data Science?
Both are important, but SQL is often tested first in interviews. Python is essential for modeling and analysis, while SQL is critical for real-world data extraction.
9. What is the difference between a Data Scientist and an AI Engineer?
A Data Scientist focuses on analysis, modeling, and insights, while an AI Engineer focuses on building, deploying, and scaling AI systems. Both roles require strong fundamentals but differ in specialization.
10. Can beginners learn AI and Data Science without a technical background?
Yes. Many successful professionals start with no coding background. A structured roadmap, simple learning approach, and consistent practice make it achievable.
11. How important are soft skills in AI and Data Science careers?
Soft skills are very important. Communication, problem-solving, and business understanding help you explain insights and work effectively with teams, which directly impacts hiring decisions.
12. What is the biggest mistake beginners make in AI and Data Science?
The biggest mistake is learning without building projects. Watching tutorials alone does not make you job-ready. Applying skills to real datasets is essential.
13. Do I need to learn cloud platforms for Data Science jobs?
For entry-level roles, cloud skills are helpful but not required. For advanced or AI engineering roles, basic knowledge of AWS, GCP, or Azure is highly recommended.
14. How can I prepare for Data Science interviews effectively?
Practice:
- Python and SQL coding questions
- Statistics and ML concepts
- Case studies
- Explaining your projects clearly
Mock interviews and regular revision help a lot.
15. What tools should I focus on first as a beginner?
Start with:
- Python
- Pandas and NumPy
- SQL
- Matplotlib or Seaborn
Avoid learning too many tools at once.





One Comment